In 2025, payment fraud losses are hitting unprecedented levels, with businesses facing increasingly sophisticated attacks and evolving liability regulations that can shift financial responsibility without warning.
Picture this: It's Monday morning, and Sarah opens her bakery as usual. By Friday, she's staring at a stack of chargeback notices totaling $50,000. Her crime? Processing chip card transactions on her old swipe-only terminal.
This scenario isn't from 2015—it's happening right now to businesses worldwide who don't understand that liability shift rules continue evolving. What started with the October 1, 2015 EMV liability shift was just the beginning. One day, banks absorbed fraud losses. The next day, unprepared merchants became the target.
The plot twist nobody saw coming? Many business owners installed chip readers after 2015 and thought, "Problem solved!" Wrong.
Here's what's catching businesses off-guard in 2025:
- New liability shifts are being implemented globally
- Online payment liability rules are becoming stricter
- Having the right equipment ≠ being protected from evolving threats
- Sophisticated fraud tactics specifically target compliance gaps
So, whether you're processing payments in Times Square or Tasmania, current liability shift rules determine who pays when fraud happens. Miss a security requirement today? You're the one writing the check tomorrow.
This article addresses two critical questions every business owner must answer now: What exactly is liability shift, and how does it work in today's payment landscape? And more importantly, what specific actions must you take immediately to protect your business from becoming liable for fraud losses?
Part 1: What is Liability Shift? Understanding Today's Payment Security Landscape
Liability shift isn't a one-time event that happened in 2015—it's an ongoing evolution that continues to reshape who pays for fraud in 2025.
What Exactly Is a Payment Liability Shift?
A payment liability shiftis a basic change in who is financially responsible if credit cardfraud happens. Rather than the customary model whereby card-issuing banks bore most fraud losses, the responsibility today falls to the payment chain member with the least secure technology or procedures.
Think of it as a "weakest link" principle in card payment security that's more relevant than ever in 2025. The party that fails to implement the most current security standards becomes financially responsible for fraudulent transactions.
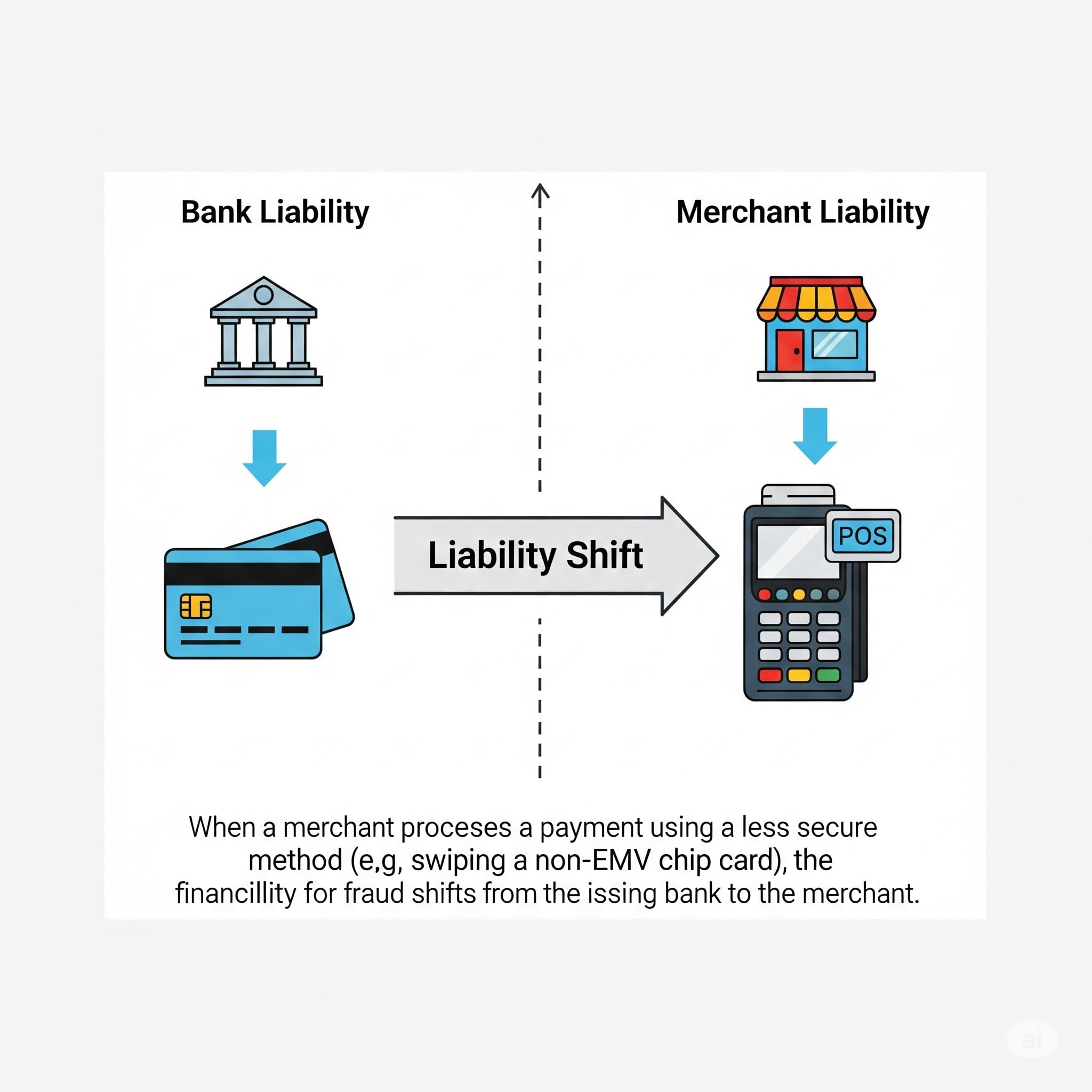
So, the core principle?The entity with the least secure payment method bears the liability for fraud losses.
This sets up a strong incentive system that encourages the acceptance of more secure payment methods throughout the whole ecosystem. Merchants, acquirers, or issuers are driven to quickly improve their systems when they understand they will be liable financially for security flaws.
The In-Store Rule: What is the EMV Liability Shift?
The EMV (Europay, Mastercard and Visa) liability shift transformed in-person card payments worldwide. While the U.S. implemented this in 2015, many other regions adopted EMV technology much earlier:
- Europe: Implemented EMV in the early 2000s
- Canada: Completed transition by 2012
- Australia: Full implementation by 2013
- Asia-Pacific: Varying timelines, with most major markets completed by 2016
How does it work?
Imagine Sarah's Coffee Shop in downtown Chicago. Before 2015, when a fraudster used a counterfeit card at her register, the bank absorbed the loss. After the EMV shift, here's what happened:
Scenario A: Sarah upgraded to EMV terminals
- Fraudster attempts counterfeit card → Terminal reads authentic chip → Transaction approved, but bank remains liable for any fraud
Scenario B: Sarah kept her old swipe-only terminal
- Same fraudulent card → Only magnetic stripe read → Transaction approved, but Sarah becomes liable for the $200 loss plus chargeback fees
The difference? A $500 terminal upgrade versus potentially thousands in fraud losses.
Are there any regional variations?
Different markets have implemented unique approaches:
- Europe: Strong emphasis on Chip and PIN
- United States: Primarily Chip and Signature initially, now moving toward PIN
- Latin America: Mixed implementation with focus on reducing cash dependency
The Online Rule: What is the 3-D Secure (3DS) Liability Shift?
For online purchases, 3-D Secure (3DS) authentication acts as the liability transfer device. By means of risk-based authentication, 3-DS 2.0—the newest edition—offers better security and user experience through enhancements.
What is the 3DS liability framework?
When 3-DS authentication is properly implemented:
- Liability typically remains with the issuing bank
- Merchants gain protection against "card not present" fraud chargebacks
When 3-DS is not implemented or fails:
- Merchants bear liability for fraudulent transactions
- Higher chargeback rates and associated fees
How global 3DS implementation has evolved and what it means for your business today:
- Europe: Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) under PSD2 made 3DS mandatory for most online transactions (2019-2021), meaning strict liability rules are now in full effect
- United Kingdom: Post-Brexit implementation of similar SCA requirements means UK businesses face the same strict liability standards
- India: Reserve Bank of India (RBI) mandated additional authentication for all card transactions, making 3DS non-negotiable for Indian market access
- Australia: Progressive merchant and issuer adoption means most major processors now expect 3DS implementation
Who is Liable? A Simple Breakdown Table.
| Transaction Type | Security Method | Merchant Implementation | Who Bears Liability | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-Person | EMV Chip | EMV-enabled terminal | Issuing Bank | Low |
| In-Person | EMV Chip | Swipe-only terminal | Merchant | High |
| In-Person | Magnetic Stripe | Any terminal | Issuing Bank | Medium |
| Online | 3DS Authentication | 3DS implemented | Issuing Bank | Low |
| Online | 3DS Authenticationp | No 3DS | Merchant | High |
| Online | Basic Authorization | Standard processing | Merchant | High |
| Contactless | EMV Contactless | NFC-enabled terminal | Issuing Bank | Low |
| Contactless | EMV Contactles | No contactless support | Merchant | Medium |
Part 2: What You Must Do Now – Immediate Actions to Protect Your Business
Understanding liability shift is only half the battle. In 2025, taking immediate protective action is what separates protected businesses from those facing devastating fraud losses.
Critical Reality Check: Why Basic Compliance Isn't Enough in 2025
The terminal is just the start. Having an EMV terminal isn't enough in today's evolving landscape. You remain exposed if:
Misconfiguration Issues
Your terminal isn't set up correctly to prioritize chip reading. Many merchants discover too late that their systems default to magnetic stripe processing, even when chips are present.
Lapsed Certification
Your software or hardware isn't currently certified. Payment technologies require ongoing certification updates:
- Level 2/3 compliance requirements change regularly
- Security patches must be applied promptly
- Terminal firmware needs regular updates
Disabled Features
You've turned off contactless or PIN functionality, creating security gaps. Some merchants disable these features due to:
- Training concerns
- Processing speed worries
- Customer preference assumptions
The Fallback Trap
Fallback transactions occur when a chip fails and the system reverts to magnetic stripe processing. These transactions carry higher liability risks and are closely monitored by card networks. Excessive fallback rates can result in:
- Increased interchange fees
- Additional monitoring programs
- Potential processing restrictions
The Digital Imperative
Online commerce faces increasingly complex liability considerations:
Strong Customer Authentication (SCA)
European regulations require additional authentication for most online transactions, with specific exemptions for:
- Low-risk transactions (under certain thresholds)
- Trusted beneficiaries
- Recurring payments with fixed amounts
Risk-Based Authentication
Modern 3-DS 2.0 systems analyze hundreds of data points to determine authentication requirements, including:
- Device fingerprinting
- Behavioral analytics
- Transaction patterns
- Geographic indicators
Your Immediate Action Plan: What to Implement Today
Don't wait for fraud to hit. These are the specific steps you must take immediately to protect your business from liability exposure.
URGENT: For In-Person Payments
-
Ensure proper EMV implementation
- Verify your terminals are EMV-certified and regularly updated
- Confirm proper configuration to prioritize chip reading
- Test fallback procedures and monitor fallback transaction rates
-
Enable modern payment methods
- Promote contactless payments (tap-to-pay, mobile wallets)
- Support multiple authentication methods (PIN, signature, contactless)
- Train staff on proper terminal operation and troubleshooting
-
Monitor transaction patterns
- Carefully manage fallback transactions—when chips fail and swipes are used
- Track unusual transaction patterns that might indicate fraud
- Implement additional verification procedures for high-value transactions
CRITICAL: For Online Payments
-
Implement robust 3-DS authentication
- Always implement and force 3-DS authentication whenever possible
- Prioritize 3-DS for high-risk transactions (large amounts, new customers, unusual patterns)
- Use intelligent risk-based authentication to balance security and user experience
-
Choose the right technology partners
- Use a payment processor that simplifies 3-DS integration
- Ensure your platform supports the latest 3-DS 2.0 standards
- Implement seamless authentication flows that don't frustrate customers
-
Advanced fraud prevention
- Deploy machine learning-based fraud detection
- Implement device fingerprinting and behavioral analytics
- Use geolocation verification and velocity checking
ESSENTIAL: Overall Strategy for 2025 and Beyond
-
Deploy advanced tools
- AI & ML: Advanced fraud detection systems
- Real-time monitoring: Immediate alerts for suspicious transaction patterns
- Multi-layered security: Combine multiple authentication and verification methods
-
Maintain strategic partnerships
- Work with certified payment processors who stay current with regulations
- Partner with fraud prevention specialists for comprehensive protection
- Maintain relationships with acquiring banks that understand your business model
-
Customer communication
- Educate customers about new security features and their benefits
- Provide clear instructions for using chip cards and contactless payments
- Communicate proactively about any changes to payment processes
Conclusion
The liability shift landscape isn't slowing down—it's accelerating. Learning about liability shift rules helps you to safeguard your income as well as to comply. Businesses that actively apply current security standards lower fraud risk and foster consumer trust as payment systems change with biometric authentication, tokenization, and strengthened security measures.
The key takeaway? Don't be the weakest link in the payment chain.
Ready to secure your payment processing and reduce liability risks? Verinite's 14+ years of experience cover the end-to-end lifecycle of card issuing and acquiring business. Our comprehensive consulting and technology solutions help businesses navigate liability shift requirements while optimizing payment security.
Contact Verinite today to protect your business from fraudulent chargebacks and ensure seamless, secure transactions across all channels.
FAQs
1. What's a payment liability shift?
It's a change in who pays when credit card fraud happens, shifting responsibility to the business with the least secure payment setup.
2. What are the two main types of liability shifts?
The two main types are the EMV shift for in-store payments and the 3-D Secure (3DS) shift for online payments.
3. How can I protect my business?
You can contact Verinite to learn how to secure your payment processing and reduce liability risks.
